Coconuts have long been prized for their versatility and rich nutrient profile. From their flesh to their water, coconuts offer an abundance of products used in both beauty and culinary industries.
Two popular derivatives are coconut milk powder and coconut water powder. Though both come from the coconut, the two serve very different purposes, both nutritionally and in the kitchen.
Understanding the difference between these two powders can help you make informed decisions for your diet and lifestyle.
In this article, we mainly break down what each powder is, how they are made, their health benefits, and how they differ in terms of nutrition, usage, and applications.
What is Coconut Milk Powder?
Coconut milk powder is derived from the liquid extracted from coconut flesh (the white, meaty part of the coconut). This liquid, usually referred to as coconut milk, is dried and processed into a fine powder.

Fig. 1: Coconut milk powder (Pixabay)
It has a rich flavor and creamy texture, similar to the coconut milk that comes in cans or cartons but with the convenience of a longer shelf life.
This process of making the powder often involves drying the coconut milk under low heat until all the moisture is removed, leaving behind a concentrated powder.
The product can be reconstituted with water to make coconut milk, or it can be used directly in cooking and baking for a creamy, tropical taste.
Essentially, this product is a popular choice for people who enjoy the creaminess and flavor of coconut milk but want something more shelf-stable.
Again, it’s commonly used in soups, curries, desserts, and smoothies, and it is a favorite among those who are following a dairy-free or plant-based diet.
What is Coconut Water Powder?
Coconut water powder, on the other hand, is made from the clear liquid found inside young green coconuts.
It is well-known for its hydrating properties and is packed with electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, and sodium (3).
To make coconut water powder, the liquid is usually freeze-dried or spray-dried, turning it into a powder form that retains most of the nutrients and flavor of fresh coconut water.
Coconut water powder is convenient for making rehydration drinks, and smoothies, or simply adding a nutritional boost to your beverages.
This product is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts because of its high electrolyte content and ability to help in hydration after exercise.
While coconut water powder may lack the richness and fat content of coconut milk powder, it is a great alternative for people looking for a light and refreshing coconut flavor with the added benefit of natural hydration.

Fig. 2: Coconut water powder (Pixabay)
Nutritional Differences Between the Two Products
One of the major differences between coconut milk powder and coconut water powder lies in their nutritional profiles. Their composition varies significantly because they come from different parts of the coconut (1).
Coconut Milk Powder Nutrition
- Calories: Coconut milk powder tends to be higher in calories because of its fat content. It is rich in saturated fats, majorly medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are known for their potential health benefits like boosting energy and supporting fat loss.
- Fat: Again, it is rich in fats, especially lauric acid, a type of fat that has antimicrobial properties.
- Carbohydrates: It contains moderate amounts of carbohydrates, mainly from natural sugars.
- Protein: It provides a small amount of protein.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Again, the product has some vitamins like vitamin C, and minerals like iron, magnesium, and potassium, though not as much as coconut water powder.
Coconut Water Powder Nutrition
- Calories: Coconut water powder is lower in calories compared to coconut milk powder.
- Fat: It has almost no fat, making it a great low-calorie, fat-free alternative for people seeking a hydrating drink.
- Carbohydrates: The carbohydrates in coconut water powder mostly come from natural sugars, offering a quick energy source.
- Electrolytes: Coconut water powder is particularly rich in electrolytes, for instance, potassium, sodium, magnesium, and calcium, which are essential for maintaining proper hydration and muscle function.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Coconut water powder is a great source of minerals, particularly potassium, which is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and heart function.
In a nutshell, if you are looking for a product that offers healthy fats and a creamy texture, coconut milk powder is the way to go.
However, if you need a light, hydrating beverage rich in electrolytes, coconut water powder is a better choice.
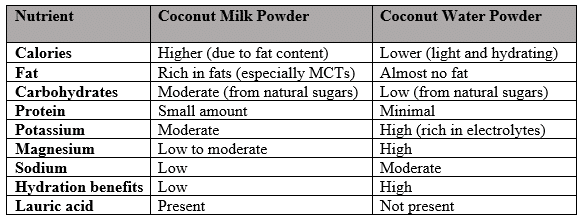
Table 1: Nutritional Comparison of Coconut Milk Powder vs. Coconut Water Powder
Production Process
The production processes for the two products differ significantly because they come from different parts of the coconut.
Coconut Milk Powder Production
The powder is produced by first extracting the coconut milk from the flesh of mature coconuts. The milk is then heated and dehydrated using a low-heat process.
Sometimes, food-grade additives or stabilizers may be added to prevent the powder from clumping or to extend its shelf life.
The result is a rich, creamy powder that can be rehydrated or used in its powdered form.
Coconut Water Powder Production
Coconut water powder is produced by freeze-drying or spray-drying the liquid found inside young coconuts. These methods help preserve the nutrients while removing the water content.
Spray-drying tends to be the more common and cost-effective method, but freeze-drying is often considered superior in terms of nutrient retention.
The end product is a light, fine powder that dissolves easily in water.
Culinary Uses of Coconut Milk Powder
Coconut milk powder is prized for its creamy texture and versatility in cooking. It can be rehydrated with water to create coconut milk or used in its powdered form to add richness to various dishes.
Some common culinary uses include:
- Curries: It can be added to curry dishes to give them a rich, creamy texture without the need to open a can of coconut milk.
- Soups: Also, a spoonful of the milk powder can turn a broth-based soup into a creamy, coconut-flavored delight.
- Smoothies: Add a tropical twist to your smoothies by mixing in a bit of the powder for flavor and creaminess.
- Desserts: Coconut milk powder can be used in baking or to make desserts like puddings and cakes.
Culinary Uses of Coconut Water Powder
Coconut water powder, due to its light and refreshing nature, is used differently from coconut milk powder. Some of its common uses include:
- Hydration Drinks: Rehydrate coconut water powder with water to create an instant electrolyte drink, perfect for after workouts or hot days.
- Smoothies: Add a boost of natural hydration to your smoothies by mixing in coconut water powder.
- Baking: While less common, coconut water powder can be used in certain baked goods to add moisture and a subtle coconut flavor.
- Frozen Treats: Again, it can be added to homemade ice pops or sorbets for a refreshing, coconut-flavored treat.
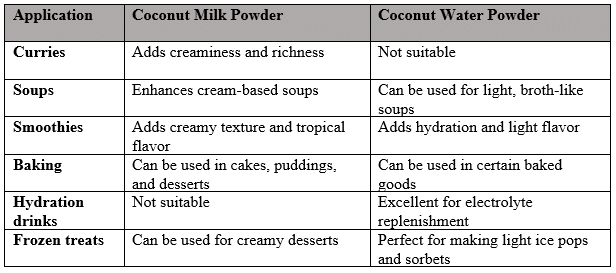
Table 2: Culinary Uses of Coconut Milk Powder vs. Coconut Water Powder
Health Benefits of Coconut Milk Powder
Coconut milk powder provides many health benefits, largely due to its fat content and nutrients:
- Rich in MCTs: The medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) in coconut milk powder are a type of fat that is quickly absorbed and used for energy. They can support weight loss and improve brain function.
- Supports Heart Health: Despite its saturated fat content, coconut milk powder contains lauric acid, which may have heart-protective effects by increasing good cholesterol (HDL).
- Dairy-Free: It is an excellent alternative to dairy milk for people who are lactose intolerant or following a vegan diet.
Health Benefits of Coconut Water Powder
Coconut water powder is well-known for its hydrating and electrolyte-replenishing properties:
- Hydration: Packed with electrolytes like potassium and magnesium, coconut water powder helps maintain proper hydration, particularly after exercise or during hot weather.
- Supports Heart Health: The potassium in coconut water powder plays an important role in regulating blood pressure, which supports cardiovascular health.
- Low-Calorie: For those watching their calorie intake, coconut water powder is a great low-calorie option that offers hydration without unnecessary fats or sugars.
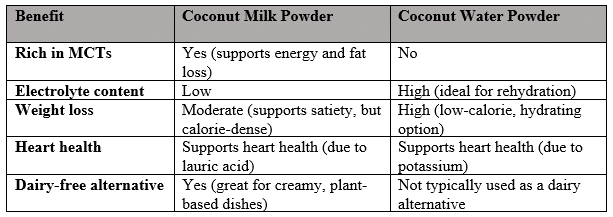
Table 3: Health Benefits Comparison
Coconut Milk Powder vs. Coconut Water Powder: Weight Loss
If you are focused on weight loss, coconut water powder may be the better option, as it is lower in calories and contains almost no fat.
Again, can provide hydration and essential electrolytes without adding significant calories to your diet.
Coconut milk powder, while higher in calories and fat, contains MCTs (2), which may support fat loss by promoting satiety and increasing metabolism.
Nevertheless, it should be consumed in moderation if weight loss is your main goal.
Comparison Regarding Hydration and Electrolytes
When it comes to hydration, coconut water powder is the clear winner. It is rich in electrolytes, mainly potassium, which is essential for maintaining fluid balance and proper muscle function.
On the other hand, coconut milk powder is more focused on providing fats and calories, so it’s not the ideal choice for rehydration after exercise or in hot weather.
Shelf Life and Storage Considerations
Coconut Milk Powder
Coconut milk powder typically has a longer shelf life compared to canned coconut milk.
It should be stored in a cool, dry place and kept tightly sealed to prevent moisture from getting in, which could cause clumping or spoilage.
Coconut Water Powder
Coconut water powder also has a long shelf life; however, it is sensitive to moisture.
Like the milk powder, it should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion
The choice between the two products depends on your needs and preferences.
If you are looking for a creamy, dairy-free alternative for cooking and baking, coconut milk powder is an excellent choice.
It is rich in fats and can add a luscious texture to a variety of dishes.
On the other hand, if you need a refreshing, low-calorie hydration boost, coconut water powder is ideal, thanks to its high electrolyte content and light flavor.
Each product has its unique strengths, so consider your health goals, dietary needs, and culinary preferences when deciding which one to incorporate into your routine.
References
1. Nevin, K. G., & Rajamohan, T. (2006). Virgin coconut oil supplemented diet increases the antioxidant status in rats. Food chemistry, 99(2), 260-266.
2. Marina, A. M., Man, Y. C., & Amin, I. (2009). Virgin coconut oil: emerging functional food oil. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20(10), 481-487.
3. Yong, J. W., Ge, L., Ng, Y. F., & Tan, S. N. (2009). The chemical composition and biological properties of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) water. Molecules, 14(12), 5144-5164.


