The organic food market has experienced remarkable growth over the past decade, reflecting a significant shift in consumer preferences towards healthier and more sustainable food alternatives.
What started as a niche market fueled by a small group of health-conscious individuals has turned into a global movement that impacts how food products are produced, marketed, and consumed.
The recent increase in demand for organic products is indicative of an ongoing shift in consumer values, as more individuals place a higher priority on ethical considerations, environmental sustainability, and health when making food decisions.
In this article, we delve into the key trends and statistics that have shaped and continue to impact the organic food industry, providing insights into its explosive growth and implications for food production and consumption.
Understanding organic food and why this topic is important
Organic food are simply food products produced without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), or artificial additives.
This makes them an appealing alternative for people who are concerned about the long-term effects of conventional farming methods on both their health and the environment.
As awareness of these issues continues growing, so too has the demand for organic products, resulting in a significant growth in the market.
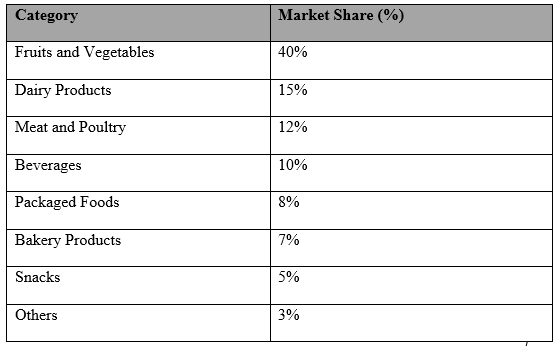
Table 1: Top Organic Food Categories by Market Share (2023) (Nielsen, 2023).
This topic is important since it shows not only the changing landscape of the food industry but also the evolving priorities of consumers.
The growth of the organic food market has implications for public health, environmental sustainability, as well as the future of agriculture, making it a major subject of interest for consumers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders alike.
Therefore, comprehending the factors that are driving this growth and the challenges it faces is vital for all stakeholders interested in the future of food.
Global Market Growth of Organic Food
In 2012, the global organic food market was valued at around $63 billion. By 2022, it had more than doubled, reaching an estimated $150 billion (Golijan & Dimitrijević, 2018). This notable growth represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8.4%.
According to Research and Markets, the organic food market is anticipated to experience rapid growth in the coming years; it is expected to grow to $489.75 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 15.1%.
This steady increase in market value demonstrates the growing consumer preference for organic products.
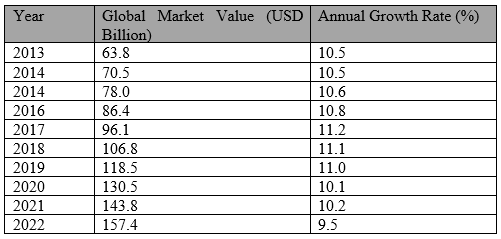
Table 2: Global Organic Food Market Growth (2013-2023) (Grand View Research, 2023).
Regional Contributions
America
The U.S. has been a key driver of this growth, consistently maintaining its position as the largest market for organic food (Euromonitor International, 2023).
In 2022, U.S. organic food sales surpassed $63 billion, accounting for over 6% of total food sales in the nation. This marks a considerable increase from about 3% in 2012 (Euromonitor International, 2023)
Canada’s organic food market has also experienced substantial growth, with increasing consumer demand and government support for organic farming methods.
In Latin America, Golijan and Dimitrijević (2018) indicate that the biggest organic product market is Brazil; markets of Argentina, Colombia, Chile, and Peru, Chile are majorly export-oriented (Euromonitor International, 2023)
Europe
Europe is considered the second-largest market for organic food, with nations such as Germany, Italy, and France leading the way.
According to Golijan and Dimitrijević (2018), the market for organic food and beverages in Europe grew by 10% in 2015, reaching a value of $31.1 billion.
The European organic food market grew by about 70% over the last decade, with strong consumer demand supported by favorable government policies promoting organic farming.
Besides, the European Union has robust policies supporting organic farming, and government subsidies have incentivized farmers to switch to organic methods.
Particularly significant market expansion has been observed in nations like the U.K., Germany, and France.
European consumers are highly cognizant of the benefits of organic food, and there is a strong cultural emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility.
Asia-Pacific
While still a smaller segment, the organic food market in Asia-Pacific is growing rapidly. Growing affluence and health consciousness are fueling the market for organic products in nations like India, China, and Japan (Euromonitor International, 2023)
Growing income levels, increased health awareness, and concerns over food safety have motivated the expansion of the organic food sector in this region.
Despite the growth, challenges including limited infrastructure for organic farming and higher costs pose obstacles to greater widespread adoption.
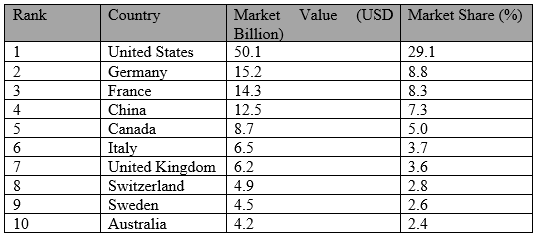
Table 3: Top 10 Countries by Organic Food Market Share (2023) (FiBL & IFOAM, 2023).
Consumer Trends Driving the Growth
The popularity of organic food has increased due to a number of factors, such as consumer awareness of environmental and health concerns and the influence of younger generations that place a higher value on sustainability.
Health Consciousness
- Health & Wellness: People are becoming more conscious of the possible health hazards linked to synthetic chemicals, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and pesticides. Organic foods, which are produced without these chemicals, have become synonymous with health and wellness.
- Dietary Preferences: Growing dietary trends including plant-based, gluten-free, and clean eating have increased consumer demand for organic products since they often adhere to these dietary guidelines.
Environmental and Ethical Concerns
- Sustainability: Organic farming methods emphasize soil health, biodiversity, and less chemical use, and are seen to be more environmentally friendly. As climate change and environmental degradation become more pressing concerns, people are choosing organic foods as a way to support sustainable farming.
- Animal Welfare: Organic food production standards usually include stricter guidelines for animal welfare, which appeals to consumers who value ethics.
Demographic Shifts
- Gen Z and Millennials: The younger generations are driving the trend of eating more organic food. Demand for organic products is being driven by these demographics, who are more inclined to prioritize sustainability, transparency, and ethical sourcing (Organic Trade Association, 2023).
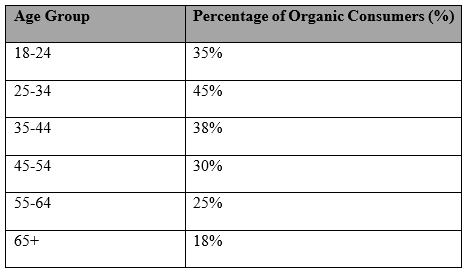
Table 4: Consumer Demographics: Organic Food Consumption (2023) (Organic Trade Association, 2023).
The Role of Retail and E-commerce
How organic food is distributed has also changed, with major players in e-commerce and retail significantly contributing to the general public’s increased accessibility to organic goods.
Retail Expansion
- Supermarket Availability: Big-box stores have increased the selection of organic foods and created whole departments devoted to them. The growth of the market as a whole has been aided by chains that specialize in organic and natural foods, such as Whole Foods Market.
- Private Label Growth: A number of retailers have developed their own private-label organic brands, providing individuals with a broader range of affordable organic products.
E-commerce Influence
- Online Sales Surge: The COVID-19 pandemic hastened the transition to online grocery shopping, especially for organic products. Organic products are now more widely available thanks to e-commerce sites like Amazon, Thrive Market, and even the online departments of conventional grocery shops.
- Subscription Services: With an emphasis on organic products, organic meal kits and subscription boxes have grown in popularity, providing customers with convenience and variety.
Regional Variations in Organic Market Growth
Over the past ten years, the organic food market has grown impressively worldwide, but the rate and factors driving this growth have varied greatly throughout geographical areas. These regional differences are influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, government policies, consumer awareness, and cultural beliefs on sustainability and health.
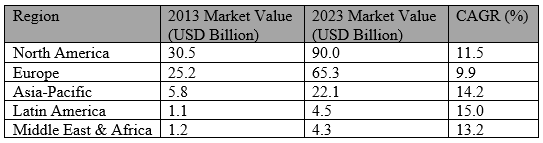
Table 5: Regional Organic Food Market Growth Rates (2013-2023) (Euromonitor International, 2023).
1. North America
United States
The U.S. is the largest market for organic food globally, with sales surpassing $63 billion in 2022. Organic food currently accounts for over 6 percent of total food sales in the nation, up from around 3 percent in 2012 (FiBL & IFOAM, 2023).
This growth has been fueled by a strong health and wellness trend, increased availability of organic products in mainstream supermarkets, as well as the rising consumer concern over pesticides and GMOs.
Customers often recognize and trust the USDA Organic certification, which also contributes to the expansion of the market.
Canada
The organic food sector in Canada has also experienced significant expansion due to similar health and environmental concerns. Both consumer demand and government policies supporting organic farming methods boost the Canadian organic sector.
2. Europe
Germany
Germany has emerged as the leading European market for organic food, owing to robust consumer demand and favorable policy measures from the government. The availability of organic products in supermarkets is widespread, and environmental responsibility and sustainability are highly valued cultural concepts.
The country has seen consistent double-digit growth in organic food sales over the past decade.
France
The organic market in France has expanded rapidly as well, almost doubling in size in the last ten years. This expansion has been mostly driven by government initiatives, such as public awareness campaigns and subsidies for organic farming.
Organic products are becoming more and more popular among French consumers as they choose healthier and more environmentally friendly lifestyles.
Italy
Italy’s rich agricultural heritage and emphasis on authenticity and quality in food have contributed to the country’s organic food market’s steady growth. The organic sector in the country is characterized by a high level of consumer trust in organic labels and a growing number of organic farms.
3. Asia-Pacific
China
China is one of the fastest-growing markets for organic food, driven by rising incomes, increased health awareness, and concerns over food safety. Despite being still modest in comparison to North America and Europe, the organic industry has grown rapidly over the last ten years, with double-digit gains in market size.
Additionally, laws to support organic farming and certification have been enacted by the Chinese government.
Japan
The market for organic foods is expanding in Japan, but more slowly than in other countries. Concerns about food safety and a desire for natural, high-quality meals are what fuel consumer interest in organic products.
Nevertheless, the high cost of organic products remains a hindrance to more widespread adoption.
Australia
Australia boasts a thriving organic food industry, bolstered by a robust agricultural sector and a growing consumer desire for natural and sustainable goods.
The nation has seen steady growth in organic food sales, with an emphasis on exporting organic products to other countries, particularly Asia.
4. Latin America
Brazil
In Latin America, Brazil is starting to take center stage in the organic food industry. The nation has seen growing domestic demand for organic products, driven by increasing health consciousness and environmental awareness.
Besides, Brazil exports a large amount of organic goods, mostly to North America and Europe.
Argentina
Argentina is a major exporter of organic goods and has a long history of farming. Though it’s still smaller than in North America and Europe, the domestic market for organic food is expanding.
Support from the government and favorable export settings have fueled the organic sector’s expansion.
5. Middle East and Africa
In Africa, South Africa is a leading market for organic food, with a growing middle class driving demand for healthier and more sustainable food options.
Although the organic industry is still in its infancy, there is room for massive growth as consumer awareness rises.
The Middle East’s organic food market is growing, especially in nations such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
The growth is fueled by an increasing expatriate population, increasing health awareness, and an emphasis on premium food products.
Nonetheless, obstacles still exist due to the high price of organic food and the low level of domestic production.
Challenges Facing the Organic Food Industry
Notwithstanding the industry’s remarkable ten-year growth, several significant obstacles could affect the organic food sector’s future. These issues range from exorbitant prices and intricate supplier chains to problems with certification and commercial viability.
1. High Costs of Organic Production
Higher Production Costs: Compared to conventional farming, organic farming usually requires more effort and careful resource management (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Because organic farmers are prohibited from using synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs), their yields are typically lower and the cost of inputs like organic seeds and natural fertilizers is greater.
Cost Premium: Because organic production is more expensive, there is a price premium for organic products (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Although some consumers are ready to pay a higher price for organic foods, the higher costs can prevent organic foods from being widely adopted, especially by low-income households.
Economic Pressures: It can be difficult for organic farming to be financially viable, particularly for small-scale farmers who could find it difficult to compete with larger, conventional growers. This may restrict the supply of organic products as well as the expansion of the organic industry.
2. Supply Chain Complexities
Limited Scalability: Because organic farming operations rely more on labor-intensive but more sustainable processes, they are usually less scalable than conventional methods (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Meeting the rising demand for organic products may become difficult as a result, particularly in areas with less established infrastructure for organic farming.
Shortages in Supply: The organic supply chain is susceptible to shortages, particularly in times of strong demand or in the event of natural disasters like pest outbreaks or droughts. Supply chain interruptions and pricing volatility may result from these shortages.
Distribution Challenges: Organic food usually needs specialized handling and distribution processes to maintain its integrity and certification status. This may make distribution and retail more expensive and complicate logistics.
3. Certification and Labeling Issues
Complicated Certification Process: Small and medium-sized farms may find it difficult to obtain organic certification because it is a demanding and frequently expensive procedure (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Countries have different certification requirements, and switching from conventional to organic farming can take years, increasing the financial strain on farmers.
Consumer Confusion: Due to the different organic certification standards and labeling used in different nations, consumers may not be sure what exactly counts as organic.
Individuals who are not aware of the distinctions between organic and conventional products may become skeptical or mistrustful of claims made regarding organic products as a result.
Fraud and Mislabeling: Sadly, the increased demand for organic products has resulted in cases of fraud and mislabeling, in which goods are sold as organic when they are not. This damages the reputation of the entire sector and erodes customer trust in organic labels.
4. Market Competition and Saturation
Competition from Conventional Brands: Large conventional food businesses have entered the organic sector as it has evolved, often buying smaller organic brands or introducing their own organic product lines.
Although this has made organic products more readily available, it has also raised questions about the commercialization of the sector and the diluting of organic principles (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Market Saturation: There is a risk of market saturation in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where organic products’ rapid rise slows down as they become more accessible and the competition heats up.
For organic farmers, this can mean lower profitability and pricing pressure.
5. Environmental and Climate Challenges
Climate Change: Organic farming is heavily reliant on environmental conditions, and the sector is seriously threatened by climate change.
Extreme weather events, changing precipitation patterns, and increased pest pressures can all have a detrimental effect on supply chain stability and organic yields.
Sustainability Challenges: Although organic farming is usually hailed as being more sustainable, it is not without its challenges.
Organic farming can require more land to produce the same amount of food as conventional farming, which can lead to land use conflicts and environmental trade-offs.
Moreover, issues with erosion of the soil, loss of biodiversity, and water consumption may still affect organic farms.
6. Limited Consumer Access
Accessibility in Developing Regions: Organic food is still considered a luxury in many developing nations because of its greater price and scarcity (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
This may limit the market’s potential for growth in these regions and worsen access disparities to wholesome, environmentally friendly food options.
Urban vs. Rural Divide: Within a country, there might be variations in access to organic food; generally, urban areas have more choices of organic items than rural areas.
This may lead to differences in who can afford organic food and reinforce the myth that organic products are exclusively available to affluent, urban consumers.
7. Regulatory and Policy Challenges
Inconsistent Regulations: Countries and regions have very different laws governing organic farming, which makes it difficult for farmers to expand into new markets.
Additionally, inconsistent standards can cause consumer misunderstanding and make it challenging for companies to comply with various certification criteria.
Lack of Government Support: While some governments have introduced subsidies and incentives for organic farming, others have been slower to provide support.
Organic farmers can find it difficult to compete with conventional growers who get subsidies and infrastructure support if they don’t receive enough government support.
Opportunities for the Future in the Organic Food Industry
Despite the challenges facing the organic food industry, there are numerous opportunities for growth, innovation, and expansion. With the growing consumer demand for food that is ethical, sustainable, and healthful, the organic food industry is ideally positioned to benefit from these developments.
1. Technological Advancements in Organic Farming
Precision Agriculture: Using technology in organic farming, such as sensors, drones, and data analytics, can maximize crop yields, cut expenses, and optimize resource use.
Organic farming methods become more effective when farmers use precision agriculture to monitor soil health, water use, and pest activity (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Biotechnology & Natural Inputs: Studies on disease-resistant crops, organic fertilizers, and natural pest management techniques can raise the sustainability and productivity of organic farming.
Biotechnology advancements in line with organic principles can assist in mitigating some of the issues related to reduced yields and increased production expenses.
2. Expansion of Organic Certification and Standards
Simplification of Certification Processes: By simplifying the certification procedure, small and medium-sized farms may find it easier to obtain organic product certification (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Governments and certification bodies can work to reduce the costs and complexities associated with organic certification, encouraging more farmers to transition to organic practices.
Global Harmonization of Standards: As the organic market becomes more globalized, there is an opportunity to harmonize organic standards across regions.
This would improve consumer trust in organic labels, promote international trade, and make it simpler for organic producers to join new markets.
3. Growing Demand for Organic Products in Emerging Markets
Market Expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America: The organic food industry has tremendous room to grow in regions like Asia-Pacific and Latin America as disposable incomes and health consciousness rise in emerging economies.
Increased consumer awareness and wider distribution networks in these areas may present organic farmers with new business prospects.
Urbanization and Changing Lifestyles: As a result of urbanization, more people are looking for quick and healthful eating options, which is changing how they consume food.
This gives organic food firms a chance to create and sell ready-to-eat organic meals, snacks, and drinks that are suited to an urban lifestyle.
4. Innovation in Organic Product Development
Diversification of Organic Offerings: The organic food market has moved beyond basic staples like fruits and vegetables, with consumers now seeking a wide range of organic products, from snacks and beverages to dairy and meat alternatives.
By diversifying their product offerings to include more inventive and varied options like plant-based organic foods, organic superfoods, and functional meals, organic food producers can profit from this trend.
Organic Private Labels: As demand for organic products grows, more retailers are launching their own organic private label brands.
This gives shops a chance to stand out in a crowded market in addition to making organic items more reasonably priced and easily available.
5. Increased Focus on Sustainability and Regenerative Agriculture
Regenerative Organic Certification: The idea of regenerative agriculture, which emphasizes enhancing soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience, is becoming more and more popular. It goes beyond organic farming.
Regenerative organic certification can be an opportunity for farmers and brands to differentiate themselves in the market by going beyond traditional organic practices (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Solutions: Organic farming practices that promote soil health and reduce greenhouse gas emissions can position the industry as a leader in climate solutions.
As consumers and governments prioritize sustainability, organic producers can benefit from carbon credits and other incentives for sustainable practices.
6. Consumer Education and Awareness Campaigns
Transparency and Storytelling: Consumers are becoming more curious about the provenance of the food they eat as well as its backstory. Organic companies can take advantage of this trend by being more open about their sourcing, agricultural methods, and environmental initiatives.
Using storytelling in digital platforms, packaging, and marketing efforts can increase consumer loyalty and trust.
Educational Initiatives: There is a chance to inform consumers about the advantages of eating organic food for their communities, the environment, and their health.
Campaigns for public awareness, alliances with health groups, and joint ventures with influencers can all contribute to increasing demand for organic goods.
7. Government Support and Policy Initiatives
Subsidies and Incentives for Organic Farming: Governments can play a crucial role in supporting the growth of the organic food industry by providing subsidies and financial incentives for organic farming.
This can inspire more farmers to embrace organic practices and help overcome the higher expenses associated with organic production.
Public Procurement and Institutional Support: Governments and institutions can drive demand for organic products by incorporating them into public procurement policies, such as school meals and hospital food programs.
This can boost consumer awareness of organic products and provide a stable market for organic producers.
8. Collaboration and Partnerships
Partnerships with Conventional Farmers: Collaborating with conventional farmers to promote the benefits of organic farming and support their transition to organic practices can help expand the organic sector.
Partnerships with agricultural organizations, research institutions, and NGOs can provide farmers with the resources and knowledge they need to succeed in organic farming.
Cross-Industry Collaborations: Organic food firms can explore partnerships with other industries, such as the beauty and wellness sectors, to create synergies and expand the market for organic products.
Collaborations between organic food and skincare firms, for instance, might draw in individuals who value sustainable and natural products in every area of their lives.
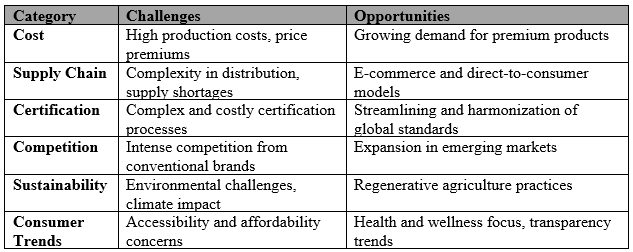
Table 6: Challenges and Opportunities in the Organic Food Industry (2023) (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
Predicted Future Trends in the Organic Food Industry
The organic food sector is well-positioned for continuing expansion and evolution as consumer preferences, technology, and global challenges impact the future of food.
It is anticipated that many significant trends, which represent changes in consumer demand, environmental consciousness, and health consciousness, will shape the organic food industry in the years to come.
Some of the most significant predicted trends for the future of organic food are discussed below.
1. Expansion of Regenerative Organic Agriculture
Beyond Organic: Regenerative agriculture is becoming more and more popular as a means of advancing organic farming. Its goals include improving biodiversity, restoring soil health, and sequestering carbon.
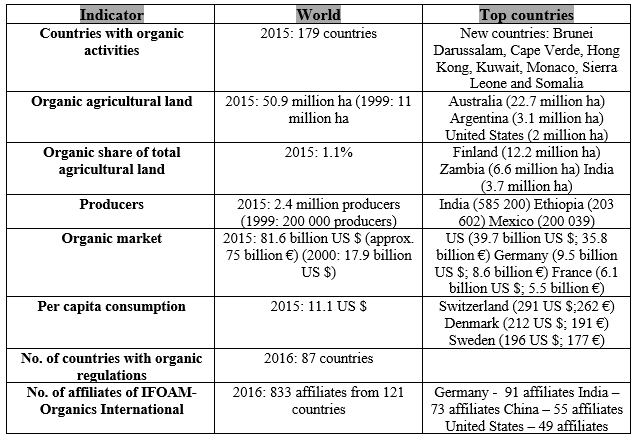
Table 7: Organic Agriculture: Key Indicators and Top Countries Source: (Golijan & Dimitrijević, 2018).
This approach goes beyond conventional organic methods by focusing on the regenerative aspects of farming, which can help mitigate climate change and improve ecosystem resilience.
2. Growth of Plant-Based Organic Foods
Plant-Based Diets on the Rise: Demand for organic plant-based products is predicted to increase as plant-based diets become more and more popular.
There is a growing trend among consumers who value sustainability and health to look for organic plant-based foods, such as snacks, ready-to-eat meals, and meat and dairy substitutes.
3. Increased Focus on Organic Convenience Foods
Organic Ready-to-Eat and Convenience Products: Demand for organic convenience foods will rise as urbanization and busy lives continue to influence consumer behavior.
This includes high-quality and conveniently packaged organic ready-to-eat meals, snacks, and beverages. Companies will have a competitive advantage if they can offer organic, healthful solutions in convenient formats.
4. Rise of Organic E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Sales
Growth of Online Grocery Shopping: The shift towards online grocery shopping, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, is expected to continue.
Organic food brands and retailers are increasingly investing in e-commerce platforms to reach consumers directly.
The convenience of online shopping, coupled with the ability to access a wider variety of organic products, will fuel further growth in this sector.
Direct-to-Consumer Models: Direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales models, where organic brands sell directly to customers via their websites, are likely to expand.
This trend enables brands to provide individualized experiences, forge closer bonds with customers, and keep control over their pricing and distribution.
5. Increased Transparency and Ethical Sourcing
Transparency as a Competitive Advantage: Individuals are demanding more transparency about where their food comes from and how it is produced.
Organic food firms that provide detailed information about their sourcing practices, supply chains, and environmental impact will build trust and loyalty with consumers.
6. Integration of Organic Products into Mainstream Retail
Mainstreaming of Organic Foods: As organic items gain popularity, they are progressively being included in big-box stores, discount stores, and supermarkets, among other mainstream retail channels.
This movement normalizes the consumption of organic food and opens up access to a larger market.
7. Focus on Health and Wellness
Organic Foods as a Health Investment: As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, more people now see organic foods as a long-term investment in their health since they are more conscious of the value of well-being and health.
This emphasis on health will continue to fuel demand for organic products that are free from harmful chemicals, additives, and GMOs.
8. Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Eco-Friendly Packaging: As individuals become more concerned about plastic waste and environmental sustainability, there will be a growing demand for organic products with sustainable packaging.
Organic companies that use recyclable, compostable, or reusable packaging will win over consumers who care about the environment.
Zero-Waste and Circular Economy Models: The organic food sector may also see the rise of zero-waste and circular economy models, where packaging is minimized or eliminated, and materials are reused or repurposed.
Innovative packaging solutions that align with the principles of sustainability will be a key differentiator in the market.
9. Greater Emphasis on Local and Regional Organic Food
Locally Sourced Organic Products: As consumers look more and more for locally sourced organic products, the “buy local” movement is predicted to gain traction in the organic food sector.
This trend supports local farmers, reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation, and enhances the freshness and quality of organic food.
Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA): There’s a good chance that community-supported agriculture initiatives, in which customers sign up to get regular deliveries of organic produce from nearby farms, will grow.
These initiatives create a more robust local food system and deeper ties between farmers and customers.
Conclusion
The surge in popularity of organic food throughout the past ten years indicates a substantial change in the priorities and values of consumers. The market for organic food is expanding due to a variety of intricately interwoven issues, ranging from sustainability and ethical concerns to health and wellness.
As this market continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the future of the global food industry, offering both challenges and opportunities for producers, retailers, and consumers alike.
The next decade will be crucial in determining how the organic food industry adapts to these challenges and continues to meet the growing demand for healthier, more sustainable food options.
References
Euromonitor International. (2023). Organic Packaged Food in the Global Market.
FiBL & IFOAM. (2023). The World of Organic Agriculture: Statistics & Emerging Trends 2023. https://www.fibl.org/en/shop-en/1254-organic-world-2023
Golijan, J., & Dimitrijević, B. (2018). Global organic food market. Acta Agriculturae Serbica, 23(46). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330779203_Global_organic_food_market
Grand View Research. (2023). Organic Food Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report, 2023 – 2030. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/organic-foods-beverages-market
McKinsey & Company. (2023). The Future of Organic Food: Challenges and Opportunities.
Nielsen. (2023). Organic Food Category Trends and Market Share Analysis.
Organic Trade Association. (2023). U.S. Organic Industry Survey. https://ota.com/market-analysis/organic-industry-survey/2023-organic-industry-survey
Research and Markets. Organic Food Global Market Report 2024. https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5939781/organic-food-global-market-report
